Deno 1.27: Major IDE Improvements
Deno 1.27 has been tagged and released with the following new features and changes:
- Language Server/IDE improvements
- Improvements to
npmcompatibility navigator.languageWeb API- Improvements to
deno task - Upgrade checker
- Changes to
DenoAPIs - Updates to
deno lint - V8 10.8
- Node.js compatibility improvements
- Changes to standard library APIs
If you already have Deno installed, you can upgrade to 1.27 by running:
deno upgradeIf you are installing Deno for the first time:
# MacOS and Linux
curl -fsSL https://deno.land/x/install/install.sh | sh
# Windows
iwr https://deno.land/x/install/install.ps1 -useb | iexClick here for more installation options.
Language Server/IDE improvements
Inlay Hints
TypeScript added support for inlay hints in version 4.4; this release of Deno exposes this functionality to the LSP. Inlay hints are small snippets of information that are added inline into your code, displaying information about your code. In a lot of ways it is an “inline hover”.
A view of code without inlay hints:
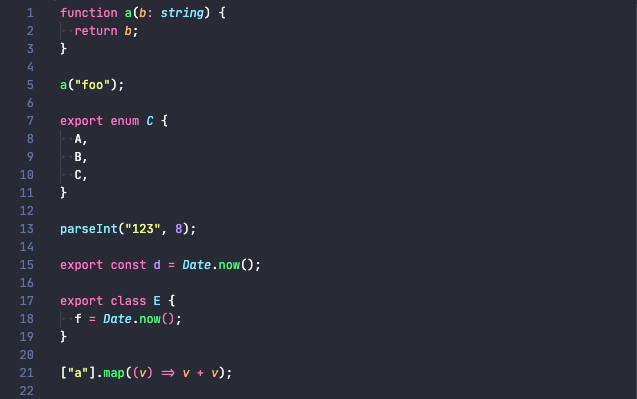
A view of code with inlay hints enabled:
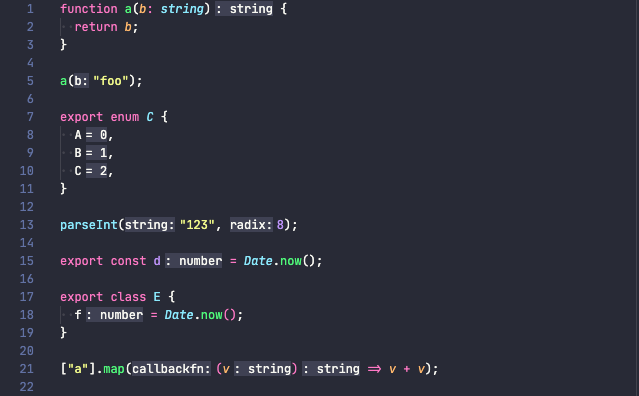
Inlay hints can make code a lot more readable, filling in gaps of information that isn’t present in code. Especially with type inference being common when working with TypeScript or type checked JavaScript, it can be really useful to “see” the hidden inferred types without having to hover over a variable to discover what it is, as well as reducing the number of explicit type annotations in the code while not decreasing the readability.
There are several options to configure the support for inlay hints which allow for customization of how inlay hints work:
deno.inlayHints.enumMemberValues.enabled- Enable/disable inlay hints for enum values. The default isfalse.deno.inlayHints.functionLikeReturnTypes.enabled- Enable/disable inlay hints for implicit function return types. The default isfalse.deno.inlayHints.parameterNames.enabled- Enable/disable inlay hints for parameter names. Values can be"none","literals","all". The default is"none".deno.inlayHints.parameterNames.suppressWhenArgumentMatchesName- Do not display an inlay hint when the argument name matches the parameter. The default istrue.deno.inlayHints.parameterTypes.enabled- Enable/disable inlay hints for implicit parameter types. The default isfalse.deno.inlayHints.propertyDeclarationTypes.enabled- Enable/disable inlay hints for implicit property declarations. The default isfalse.deno.inlayHints.variableTypes.enabled- Enable/disable inlay hints for implicit variable types. The default isfalse.deno.inlayHints.variableTypes.suppressWhenTypeMatchesName- Suppress type hints where the variable name matches the implicit type. The default istrue.editor.inlayHints.enabled- Controls whether inlay hints are enabled in VS Code. Values can be"off","offUnlessPressed","on", or"onUnlessPressed".
Visual Studio Code supports inlay hints and the latest release of the Deno VS Code extension supports the configuration options. You will need to check with out editors and plugins to see if they support inlay hints and how to set the configuration options.
Registry completions
While not tied specifically to the release, we recently improved registry
completions in editors that support it. Now when typing a third party module
name from deno.land/x in an intelligent editor, the search engine which powers
the module search on deno.land is used, as well as providing a module
description and popularity information.
There are also improvements when completing the import path, where documentation
information is integrated into the display text and is also available on
hovering over an import. Third party module authors can use the @module JSDoc
tag in the first JSDoc block at the top of the module to provide this
information all the way through to the editor.
In Visual Studio Code, registry completions for deno.land/x are enabled by
default. Check how to configure deno.suggest.imports.hosts in other editors to
make sure that https://deno.land is enabled to get the completions.
Take a peek at the video to see it in action:
Bug fixes
There are several bug fixes in this release related to the language server. Specifically the language server was not properly handling “snippet” strings which is now fixed. There were several issues when performing auto-imports and code completion in JSX that caused odd behaviors which are now fixed.
Improvements to npm compatibility
This release continues the steady improvement of using npm packages in Deno.
Type checking and LSP support
Deno will now automatically pull in TypeScript types from npm packages that distribute types.
For packages that don’t distribute types, you can use a @deno-types directive
above the import in order to specify the corresponding
@types package
if one exists:
// @deno-types="npm:@types/chalk@4"
import chalk from "npm:chalk@4";For packages that require @types/node, you can specify a triple-slash
reference-types directive to pull in Node types:
/// <reference types="npm:@types/node" />
// @deno-types="npm:@types/express@4"
import express from "npm:express@4.18";Note that by doing this, Deno will use Node’s global types (ex.
setTimeout(...): NodeJS.Timeout) instead of a browser compatible types (ex.
setTimeout(...): number) in the types for npm packages. These globals will be
isolated to the npm packages and shouldn’t affect the types of your Deno code.
Node-API
Deno now supports Node-API
(formerly N-API) when used within npm packages. Node-API is a way to use native
code in Node.js. It means that packages like parcel, sqlite3, usb or
fs-xattr can now be used with Deno.
Note that this feature requires the --allow-ffi flag.
Lockfile v2
npm package resolution and integrities are now stored when using a lockfile.
# lock.json will include information about npm packages referenced in main.ts
deno cache --lock=lock.json --lock-write main.tsNote that in the 1.28 release we are planning to write a lockfile by default if you are using a deno.json file. Follow issue #11971 for updates.
Dist tags in npm specifiers
The npm registry allows tagging versions with a name. For example,
express has a “next”
tag which, at the time of writing this, has tagged version 5.0.0-beta.1.
You can now specify these dist tags in version requirements for npm specifiers.
// will import 5.0.0-beta.1 at the time of writing this
import express from "npm:express@next";Note that dist tags are still not supported if they appear in a package’s package.json. This is a bug and will be resolved soon. Follow issue #16321 for updates.
Caching npm specifiers directly via arguments to deno cache
deno cache now supports providing npm specifiers on the command line:
deno cache --unstable npm:chalk@5 npm:expressThis will download the package information and resolved versions of those packages to Deno’s global npm cache.
navigator.language Web API
Deno v1.27 adds the
navigator.language
API. It’s a read-only property that returns a string representing the user’s
system preferred language.
$ deno
> navigator.language
"en-EN"The returned string that represents the language is a BCP 47 tag.
The value returned by this API can be influenced by environment variables that
set the system locale, for example LC_ALL.
$ LC_ALL=es_ES deno
> navigator.language
"es-ES"Additionally,
navigator.languages
API is supported as well. It returns an array of preferred locales with first
value being identical to navigator.language.
Thanks to Luca Matei Pintilie for contributing this feature.
Improvements to deno task
The warning stating “deno task is unstable and may drastically change in the
future” has been removed. deno task has proven useful and won’t drastically
change going forward. That said, we may introduce some changes in its
environment to make things easier going forward such as new cross platform
commands or environment variables.
INIT_CWD environment variable
When a task is executed, it will have the same current working directory as the
deno.json the task is defined in. This may not be desired in certain
scenarios, or you may want to know what directory the user ran the task in. This
is now possible by using the INIT_CWD environment variable, which will be set
with the full path to the directory the task was run in, if not already set.
This aligns with the same behavior as
npm run.
For example, the following task will change the current working directory of the
task to be in the same directory the user ran the task from and then output the
current working directory which is now that directory (remember, this works on
Windows too because deno task is cross platform).
{
"tasks": {
"my_task": "cd $INIT_CWD && pwd"
}
}Task will now fail on async command failure
You may have used deno task to start multiple commands at once, by using an
async command:
{
"tasks": {
"start": "deno run --allow-net server.ts & deno run --allow-net client.ts"
}
}Previously, if the async command failed, the other would continue running and
you might not notice. This was in line with how most shells work, but it’s not
practical for the purposes of deno task.
Starting in this release, if an async command fails then it will also fail the
entire task. Note that if you want the previous behavior, you can opt out by
adding || true to the end of a command, which will force a 0 exit code:
{
"tasks": {
"start": "deno run --allow-net server.ts || true & deno run --allow-net client.ts || true"
}
}sleep time suffixes
The sleep command in deno task now supports providing a suffix to the time
argument as specified in the
linux man pages for sleep.
Thanks to @sigmaSd for contributing this feature.
Upgrade checker
Deno ships with the deno upgrade subcommand that allows you to easily get the
latest version of Deno. Starting with this release, Deno will now automatically
check for new versions and prompt you if one is available.
$ deno run app.ts
A new release of Deno is available: 1.26.2 → 1.27.0
Run `deno upgrade` to install it.We took special care to ensure that these checks don’t impact the performance of
your applications - they only happen in the background at most once a day. This
feature can be disabled entirely by setting the environment variable:
DENO_NO_UPDATE_CHECK=1
Changes to Deno APIs
API stabilizations
The following APIs have been stabilized in this release and no longer require
the --unstable flag to be used.
Deno.consoleSize()Deno.futime()Deno.futimeSync()Deno.loadavg()Deno.osRelease()Deno.stdin.setRaw()Deno.utime()Deno.utimeSync()
Other updates
Deno.kill()no longer requires an argument, it will default to sending aSIGTERMsignal if argument is omitted.Deno.getGid()was renamed toDeno.gid(), in preparation for stabilization of this APIDeno.getUid()was renamed toDeno.uid(), in preparation for stabilization of this APITcpListenOptions.reusePortoption was added. It allows multiple processes to listen on the same address and port. This option requires the--unstableflag and is supported only on Linux.
Updates to deno lint
The built-in linter got a new “compact” report format, that might be familiar to
users of ESLint. You can use this format by providing the --compact flag to
the deno lint subcommand.
$ deno lint --compact
/dev/deno/foo.js: line 1, col 10 - `foo` is never used (no-unused-vars)
Found 1 problem
Checked 1 fileAdditionally you can specify which report type you prefer inside your
deno.json file:
{
"lint": {
"report": "compact"
}
}Thanks to Brenley Dueck for contributing this feature.
V8 10.8
This release upgrades to the latest release of V8 (10.8, previously 10.7).
The most notable new feature in this release is support for the Change Array by copy proposal
Node.js compatibility improvements
On October 25, Node.js 18 entered Long Term Support (LTS) with version 18.12.0. In Deno v1.27, the Node.js compatibility layer’s test suite has been updated to match Node.js v18.12.0, meaning that Deno is capable of running the latest Node.js LTS release.
Please note that the entire Node.js compatibility layer still requires the use
of the --unstable flag.
Other updates
The
readline/promisesmodule has been implemented. This module provides a Promises based API for thereadlinemodule. Thanks to @PolarETech for contributing this feature.'base64url'encoding is now supported byhash.digest()in thecryptomodule. Thanks to Deniz Akşimşek for contributing this feature..nodemodules can now be loaded. See also (Node-API support)[#node-api].Better Windows support has been added for
fs.access().The
windowsVerbatimArgumentsoption has been added to thechild_processmodule’s APIs.
Changes to standard library APIs
In this release, several deprecated APIs have been removed:
The
hashmodule has been removed. The functionality of this module is available via thecryptomodule.The
textprotomodule has been removed.BSNodehas been removed from thecollectionsmodule in favor ofBinarySearchNode.BSTreehas been removed from thecollectionsmodule in favor ofBinarySearchTree.RBNodehas been removed from thecollectionsmodule in favor ofRedBlackNode.RBTreehas been removed from thecollectionsmodule in favor ofRedBlackTree.directionhas been removed from thecollectionsmodule in favor ofDirection.CSVStreamhas been removed from theencodingmodule in favor ofCsvStream.The
CSVStreamOptionstype has been removed from theencodingmodule in favor of theCsvStreamOptionstype.The
encoding/csv_stringify.tsfile has been removed in favor of theencoding/csv.tsfile and other APIs.JSONValuehas been removed from theencodingmodule in favor ofJsonValue.JSONParseStreamhas been removed from theencodingmodule in favor ofJsonParseStream.JSONStringifyStreamhas been removed fromencodingmodule in favor ofJsonStringifyStream.ConcatenatedJSONParseStreamhas been removed from theencodingmodule in favor ofConcatenatedJsonParseStream.The
listenAndServe()andlistenAndServeTls()functions have been removed from thehttpmodule in favor ofserve()andserveTls(), respectively.The streaming functionality in the
iomodule has been removed in favor of thestreamsmodule.The functionality in the
bufio.tsfile of theiomodule has been removed in favor of thebuffer.tsfile.The functionality in the
ioutil.tsfile of theiomodule has been removed in favor of theutil.tsfile.The
LineStreamclass has been removed from thestreamsmodule in favor ofTextLineStream.All benchmarking APIs have been removed from the
testingmodule in favor ofDeno.bench().The
assertThrows()andassertRejects()functions that take a callback function have been removed from thetestingmodule in favor of their other signatures.The
generate()function has been removed from theuuidmodule in favor of the WebCryptorandomUUID()function.
Thanks to Asher Gomez for contributing these changes.
